Alopecia, or hair loss, can be distressing, especially for women. They often link their hair with identity and femininity. Understanding alopecia is crucial for coping and seeking treatment. This blog post explores causes, types, and treatment options for alopecia in women. It also discusses how Wigshe can help those experiencing hair loss.
Causes of Alopecia in Women:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: This is the most common form of hair loss in women, often referred to as female pattern baldness. It is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors.
- Alopecia Areata: This is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss in patches.
- Telogen Effluvium: This type of hair loss occurs when a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle simultaneously, usually triggered by stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
- Traction: Excessive pulling or tension on the hair follicles, often from tight braids or ponytails, causes this type of hair loss.
- Other Causes: Other factors such as certain medications, nutritional deficiencies, and underlying medical conditions can also contribute to hair loss in women.
Types of Alopecia in Women:
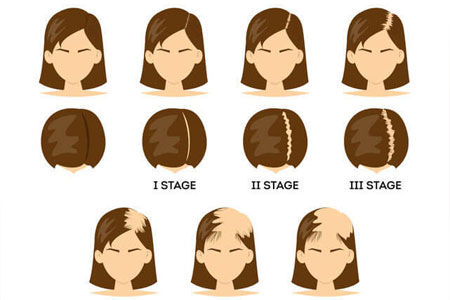
- Androgenetic Alopecia: This type of hair loss typically starts with a widening part and thinning at the crown. It can progress to more severe hair loss over time.
- Areata: This condition often presents as round, smooth patches of hair loss on the scalp, but it can also affect other areas of the body.
- Diffuse Hair Loss: This type of hair loss is characterized by a general thinning of the hair across the scalp, rather than specific patches of baldness.
Treatment Options for Alopecia in Women:
- Topical Treatments: Minoxidil, a topical medication, can help stimulate hair growth and is a common treatment for androgenetic alopecia.
- Oral Medications: Finasteride, an oral medication, can effectively treat androgenetic hair loss in women. However, doctors do not recommend it for pregnant women due to potential risks to the fetus.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For alopecia areata, corticosteroid injections into the scalp can help stimulate hair growth in affected areas.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of severe or permanent hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be an option. This surgery involves transplanting hair follicles from one part of the scalp to balding areas.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress levels, and avoiding hairstyles that cause tension on the hair follicles can help prevent and manage hair loss.
In Conclusion:
Alopecia in women can have a significant impact on self-esteem and quality of life. However, understanding the causes and treatment options can help women manage this condition effectively. If you are experiencing hair loss, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
More To Read: www.Alopecia.com